At Bay Bariatrics, we offer several types of life-changing bariatric operations. Many of our patients come to us frustrated, feeling hopeless after trying so hard to lose weight but not being able to. Our compassionate bariatric surgeons understand how you feel, and we want to help you reach your ideal weight and live a happy, healthy life. There is hope, and you have several options when it comes to bariatric surgery. One procedure we offer at Bay Bariatrics that may be right for you is called SADI-S (Single anastomosis duodenoileal bypass with sleeve gastrectomy). SADI-S is an innovative procedure for morbid obesity based on biliopancreatic diversion, in which a sleeve gastrectomy is followed by a duodeno-ileal diversion from end to side. Give us a call today to schedule your appointment and see if SADI-S is the right bariatric surgery for you.
SADI-S Weight Loss Surgery
Benefits of SADI-S
Feel healthier and gain confidence
Resume activities that were problematic.
Be more active
Reduce or eliminate diabetes.
Improved cardiovascular health
Reduced risk of intestinal leakage
Less time in surgery
Advantageous procedure for patients with 50+ BMI
Lower the risk of nutritional deficiencies
Kattie Flint
Before the surgery, I was very unhealthy and depressed. I have two kids that I couldn’t even play with because I hurt too much. I was up to 350 lbs. and I am now 180, and I can run and play with my kids.
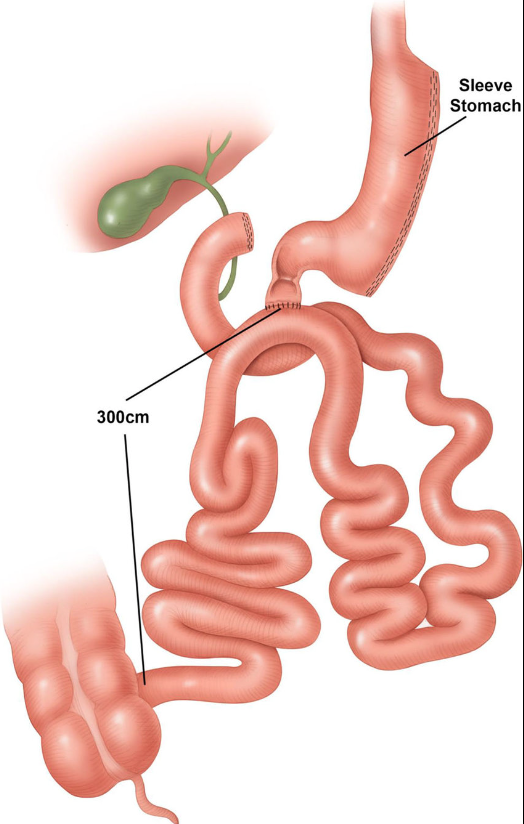
SADI-S (Single anastomosis duodenoileal bypass with sleeve gastrectomy) is a newer kind of duodenal switch operation which has helped obese individuals regulate their weight for the past three decades. The main advantage of SADI-S is that it only requires one intestinal bypass rather than two, which saves time in surgery and reduces the risk of intestinal leakage.
With this revolutionary surgical approach, the surgeons at Bay Bariatrics accomplish outstanding outcomes. The advantage of this laparoscopic or robotic operation is that it combines the excellent outcomes of sleeve gastrectomy and intestinal bypass, resulting in substantially more healthy weight loss than either sleeve or bypass alone. Because this operation has two distinct parts, it can be both a single-stage operation and a revision operation for patients who fail to lose enough weight with a sleeve alone.
In the sleeve gastrectomy portion, the stomach is slimmed down to a cylinder-shaped “sleeve” that can store substantially less food in the first stage of the procedure. Not only does the gastric sleeve result in a significantly smaller stomach, but it also suppresses the appetite-stimulating hormone ghrelin.
In the bypass portion of the operation, the first part of the intestines is bypassed, resulting in changes in gut hormones that improve glucose metabolism and help to resolve chronic conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure.

More FAQs About SADI-S
What are some of the advantages of SADI-S?
One of the advantages of the surgical procedure is versatility. SADI-S can be performed in one or two stages. When a two-stage approach is chosen, it allows the patient to lose weight in the months leading up to the final intestinal rerouting treatment, also known as a malabsorption procedure, which shortens the path that digested food travels through the intestines. A patient’s new stomach sleeve is sewn to a loop of the small intestine during malabsorption surgery, bypassing most of the small intestines. The bypass routes food through the intestinal loop (which is only 10 feet of the small intestine,) allowing the body to absorb fat and calories in less time and distance.
Because SADI-S bypasses less of the intestine than other forms of bariatric surgery, your body will be able to absorb more nutrients. There is also less possibility of contents leaking from the gut into the body cavity with SADI-S since just one new intestinal connection is created. This single connection also eliminates the risk in the future of intestinal blockage, sometimes known as an internal hernia. Since the procedure is done laparoscopically, it is minimally invasive and carries fewer risks than an open surgery.
When was the SADI-S procedure developed?
The first time SADI-s was described in medical literature was in 2007. It was initially introduced as a modification of the duodenal switch surgery. After seeing encouraging results in weight loss and other metabolic improvements, many bariatric surgeons have replaced the duodenal switch and other types of biliopancreatic diversion with SADI-s.
What is the difference between Duodenal Switch and SADI-S?
Both surgical procedures involve a sleeve gastrectomy and intestinal bypass. The classic duodenal switch has been a standard operation for many years but never achieved widespread use because of its complexity and slightly higher complication rate. The modified switch, also known as “SADI-S” or “Loop DS,” is the most recent procedure approved by the American Society of Metabolic Surgery. The SADI-S procedure is similar to a traditional duodenal switch but has been simplified and improved so that there is just one anastomosis and a significantly larger intestinal length (250-300 cm versus 100 cm) to absorb the foods you consume.
What is a pancreatic diversion?
BPD (Biliary Pancreatic Diversion) is a type of bariatric surgery used to treat obesity. It entails removing a portion of the stomach to limit the amount of food the stomach can store, as well as redirecting the GI tract past sections of the small intestines to reduce calorie absorption.
How fast do you lose weight with SADI-S surgery?
In just three months, patients often lose 30% of their excess weight, and in just one year, they drop 80%. While other bariatric operations can result in weight gain, DS individuals are the least likely to gain weight after surgery.
Is duodenal switch the same as gastric bypass surgery?
During a gastric bypass surgery, a surgeon reduces the size of the stomach by forming a smaller pouch and connecting it to the small intestine directly.
On the other hand, a duodenal switch entails “bypassing” much of the small intestine, where nutrients are absorbed. Patients who have undergone the operation are at a higher risk of malnutrition and vitamin deficiencies in the future. Therefore they must pay special attention to their food, according to the researchers. Studies show that SADI-S has fewer long-term vitamin deficiencies than traditional switch and is more similar to gastric bypass.
What are the pros and cons of duodenal switch?
Duodenal switch surgery provides a number of benefits that help you lose weight and protect your health. The benefits include:
- Patients with a very high body mass index (BMI) and severe or numerous health risks will benefit the most.
- The opportunity to consume bigger meals than with other, more restricted techniques like gastric bypass, resulting in a higher sense of fulfillment.
- Can help you shed up to 85% of your excess body weight
- Lower risk of bowel obstruction
While duodenal switch surgery may be appropriate for you, there are certain factors to consider:
- Whether you need the kind of dramatic weight loss that this operation can provide. Patients with class II and class III obesity are likely to benefit the most.
- Like other bariatric operations, sugars and sweets can cause dumping syndrome after eating, which includes nausea, weakness, sweating, anxiety, and heart palpitations. While they are seldom harmful to one’s health, they can be inconvenient or painful. Because SADI-S preserves the valve at the bottom of the stomach called the pylorus, this issue is rare.
- Protein, fat-soluble vitamins (A, E, D, and K), iron, calcium, vitamin B-12, and folic acid are among the nutrients, vitamins, and minerals that are hampered by bypassing a substantial portion of your gut. Supplements will be required on a daily basis.
- Overeating can cause the stomach pouch to stretch.
Is SADI-S covered by insurance?
The American Society of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS) recently endorsed this technique and called for insurance companies to cover this procedure. Most insurance companies still consider it experimental and will not cover it since it is so new. However, this is very likely to change.
Who is a good candidate for SADI-S?
Patients with a high BMI (>45) or diabetes are generally good candidates for SADI-S. This is also a wonderful choice for sleeve patients who have gained weight after their sleeve gastrectomy.
Is SADI-S worth it?
Overall, the benefits and results of the SADI-S procedure far outweigh any potential disadvantages. Patients report increased quality of life, reversal of health conditions, improvement in metabolic disorders, improved self-esteem, and more after achieving significant weight loss following SADI-S. Call our office today to schedule an appointment to discuss this procedure and find out if it is right for you.
What are the risks of SADI-S?
Single anastomosis duodenoileal bypass surgery, like any other surgery, carries some risks, including:
- Anesthesia and surgery carry risks such as bleeding, blood clots, and death.
- Patients who have duodenal switch surgery have a higher-than-normal risk of gallstones and gallbladder disease.
- Bowel movements may become more watery and frequent as the intestines adapt. This issue may improve over time, but it may be permanent. Even patients affected by this rarely have more than three bowel movements a day.
- Bloating in the abdomen and foul-smelling feces or gas
- Intestinal discomfort and ulcers are more likely.
If you want to know if SADI-S is right for you, talk to your doctor. Our bariatric staff is available to assist you with your weight loss goals.
What is single anastomosis duodeno ileal bypass?
The single anastomosis duodenal switch is a modification or improvement on the biliopancreatic diversion with a duodenal switch. It works to restrict and control appetite by forming a sleeve gastrectomy. The intestines are then redirected after the sleeve, similar to a gastric bypass resulting in changes in gut hormones and metabolism so that you can lose weight without feeling hungry all the time.

Deb Campbell
I battled my weigh for decades trying all kinds of ad diets and different programs only to lose weight and gain it all back again. I had high blood pressure, high cholesterol, borderline diabetes, constant fatigue, and severe joint pain. This surgery was life-changing for me. I no longer have high blood pressure, or high cholesterol, and am not borderline diabetic. My energy level is fantastic.
